A theory of change to directly incentivize villages and others to reduce the threat of wildlife hunting and increase the populations of wildlife had assumptions and results tested over four years in Laos.
The study provided evidence that the approach taken was successful and also provided ways to adapt management to achieve even better outcomes. Click here for a short video that puts the study into context.
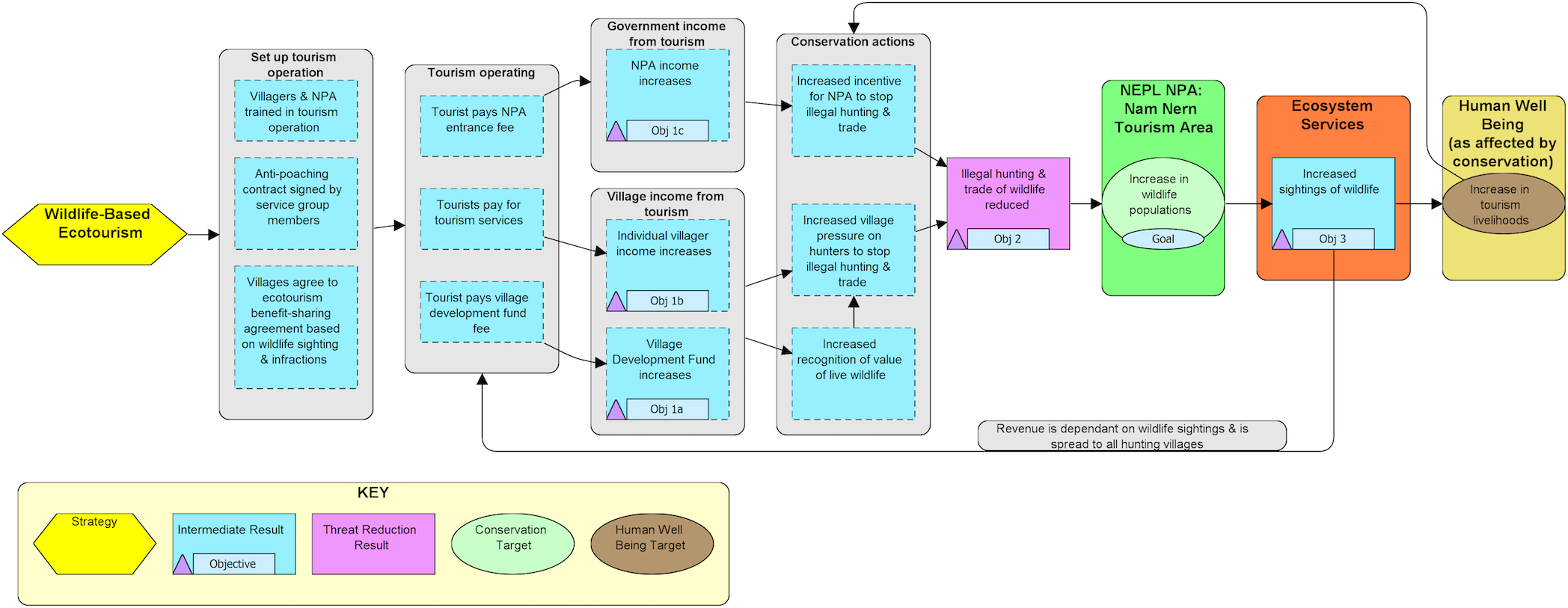
Results chain illustrating the theory of change for a direct payments model for wildlife-based ecotourism strategy.
Abstract
Ecotourism as a strategy for achieving biodiversity conservation often results in limited conservation impact relative to its investment and revenue return. In cases where an ecotourism strategy has been used, projects are frequently criticized for not providing sufficient evidence on how the strategy has reduced threats or improved the status of the biodiversity it purports to protect. In Lao PDR, revenue from ecotourism has not been directly linked to or dependent on improvements in biodiversity and there is no evidence that ecotourism enterprises have contributed to conservation. In other developing countries, direct payments through explicit contracts in return for ecosystem services have been proposed as a more cost-effective means for achieving conservation, although further research is needed to evaluate the impact of this approach. To address this need, a new model was tested in the Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area (NPA) in Lao PDR using a direct payments approach to create ecotourism incentives for villagers to increase wildlife populations. Over a four-year period, we monitored along a theory of change to evaluate assumptions about the linkages between intermediate results and biological outcomes. Preliminary results show a negative correlation between ecotourism benefits and hunting infractions in target villages; no increase in hunting sign in the ecotourism sector of the NPA relative to a threefold increase in hunting sign across the NPA’s non-tourism sectors; and an overall increase in wildlife sightings. This case provides key lessons on the design of a direct payments approach for an ecotourism strategy, including how to combine threat monitoring and data on wildlife sightings to evaluate strategy effectiveness, on setting rates for wildlife sightings and village fees, and the utility of the approach for protecting very rare species.
Citation
Eshoo PF, Johnson A, Duangdala S, Hansel T (2018) Design, monitoring and evaluation of a direct payments approach for an ecotourism strategy to reduce illegal hunting and trade of wildlife in Lao PDR. PLoS ONE 13(2): e0186133. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186133
